Carbon Neutrality

Carbon neutrality has become an increasingly significant topic in recent years, as concerns about climate change and the environmental impact of human activities have gained traction. In simple terms, carbon neutrality refers to the state or process of achieving a balance between the amount of carbon dioxide emissions produced and the amount of carbon dioxide removed or offset from the atmosphere. It encompasses a range of practices and initiatives aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions and combating warming. But why is this balance so crucial, and how can we pave the way towards a greener future?
The Earth’s mere balance is under threat due to excessive carbon emissions, primarily from industries, transportation, and deforestation. These emissions trap heat within the Earth’s atmosphere, leading to global warming, erratic weather patterns, rising sea levels, and a myriad of other ecological imbalances. The consequences are not just environmental, they encompass socio-economic consequences, from dropping agricultural yields to forced migrations and economic downturns. Simply put, our current trajectory is unsustainable, jeopardizing the very fabric of life as we know it.
To grasp the concept of carbon neutrality, it is essential to understand its underlying principle. At its core, carbon neutrality revolves around the goal of achieving net-zero carbon emissions. In other words, the aim is to neutralize or offset any carbon dioxide emissions released into the atmosphere. This involves striking a delicate balance between the amount of carbon dioxide produced and the amount that is absorbed, removed, or mitigated through various means. By striving for carbon neutrality, individuals, organizations, and even entire communities can make a significant contribution to combating climate change.
India’s Climate Goals and Commitment to Carbon Neutrality
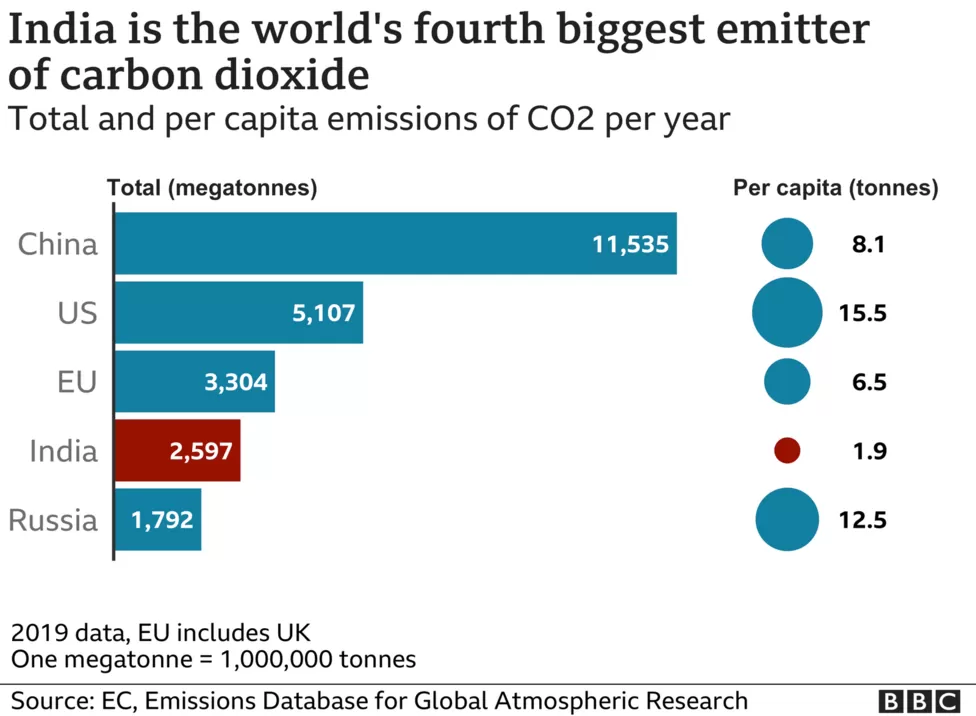
Among the leading contributors to this global challenge is India, currently the world’s fourth-largest emitter of CO2. This dubious distinction underscores the urgency with which India must act to mitigate its environmental impact, not just for its own population of over 1.3 billion people but for the global community as a whole. India has set ambitious goals to curb its carbon emissions.
The most notable of these is the commitment to achieve Net Zero by 2070. This target aligns with global efforts to limit the rise in global temperatures to well below 1.5 – 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels, as outlined in the Paris Agreement.
Energy-efficient technologies and practices can help reduce the amount of energy consumed, thereby decreasing carbon emissions. This can be achieved through measures such as upgrading energy-efficient appliances, utilizing smart building systems, and implementing energy management strategies. Additionally, simple actions like turning off lights when not in use, optimizing heating and cooling, and reducing standby power can also contribute to significant energy savings.
While it is crucial to reduce carbon emissions at their source, it is also important to explore strategies for offsetting and removing carbon from the atmosphere. Carbon offsetting involves investing in projects that reduce greenhouse gas emissions, such as reforestation, renewable energy projects in developing countries, or carbon capture and storage initiatives. These projects help to compensate for the remaining emissions that cannot be eliminated. On the other hand, carbon removal technologies, such as direct air capture or enhanced weathering, actively remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, further contributing to carbon neutrality.
Carbon neutrality is a vital step towards mitigating the effects of climate change and creating a sustainable future for generations to come. By embracing renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, offsetting carbon emissions, and promoting sustainable practices, we can work towards reducing our carbon footprint. It is imperative that individuals, businesses, and governments collaborate and take concrete actions to achieve carbon neutrality, ensuring a healthier and more sustainable planet for future generations.




